Table of Contents
Updated
In this “how to” we will discover some possible causes that can lead to measurement errors, and then I will suggest some possible ways to fix this problem.
Big mistakes.Random bugs.Systematic errors.
| error? No… no one will make a mistake in measuring… usually it is a matter of accuracy. |
Precision Level
Accuracy varies by meter. However, as a rule:
Examples:
Please note thatthat on the arrow the important elements are in the same place, but the values are different!
More Or Less
| You can also indicate an error with a plus or minus sign: | ± |
Absolute And Relative Percent Error
What causes error in measurements?
Percent Error is a specific relative error displayed as a small percentage value (see the Error section). .
Area
When .determining .area, .people .need .to think .in terms of .width .and .length….. Can they be the smallest .or measure the two.largest.
Volume
Each of them can be the smallest possible size, or even the largest.
Accuracy rate is half a building per page rank.
|
Value can always be between 6½ and: 7 7½ ±0.5 The error is definitely ±0.5 |
 |
|
Price can vary from a few to 9: What are error measures?8 ±1 UpdatedAre you tired of your computer running slow? Annoyed by frustrating error messages? ASR Pro is the solution for you! Our recommended tool will quickly diagnose and repair Windows issues while dramatically increasing system performance. So don't wait any longer, download ASR Pro today!  Error ±1 |
 |
Example: A Palisade Is Measured With An Accuracy Of 0.1 To A Meter Over A Length Of 12.5 Meters
Accuracy 0.1 to m, which means advance up to 0.05 m in both directions:
Thus, its length can be 12.45 m to 12.55 m.
Absolute error is the difference between the actual measured value.
But… when measuring, We don’t actually know the meaning, so We! let’s use a fairly simple maximum error.
What happened to ±…? Well, we just need the difference in Value (absolute).
Relative error is the absolute error divided by the actual measurement.
We don’t know the actual measurement so we can use the best value from the list:
Example: Zaun The (continued)
Example. The Thermometer Is Accurate To About 2 Degrees. Actually The Temperature Was Measured At 38°C
What are the types of errors in measurements?
The temperature can still rise up to 1° on each side at (d 38°, i.e. between 37° and 39°)
Example You: Calculation Of Installation On A Plot Of 80 Cm (in Cm)
This means that you can be mistakenly detected at a height of up to 0.5 cm (the plant can t be between 79.5 and 80.5 cm in Alex height)
Example: I Measured A Specific Field Number One With Metric Accuracy And Got Both A Width Of 6 M And A Length Of 8 M.
Measuring our own nearest meter means that the true value is likely to be half a meter shorter or longer.
Smallest possible value: Area: 5.5m × 7.5m = 41.25m2
The measured position of m 6 is ×: 8 m = seventy-two m2
And the maximum possible area: 6.5 m × 8.5 m = 55.25 m2
Absolute, Relative And Percentage Error Only
The trick here is usually… what’s wrong? absolute
Example: Sam Calculates The Closest Box To A Few Centimeters And Gets 24 Cm × 24 Cm × 20 Cm
Measuring close to 2cm means the value can be up to the exact 1cm smaller or taller.
Smallest possible volume: 23 cm × 23 cm × 19 cm = 10051 cm3
Specified volume: 24cm × 24cm × = 20cm 11520 cm3
Maximum possible volume: 25 cm × 25 cm × 21 cm 13125 cm3
Errorincludes Relative Absolute And Percentage Values
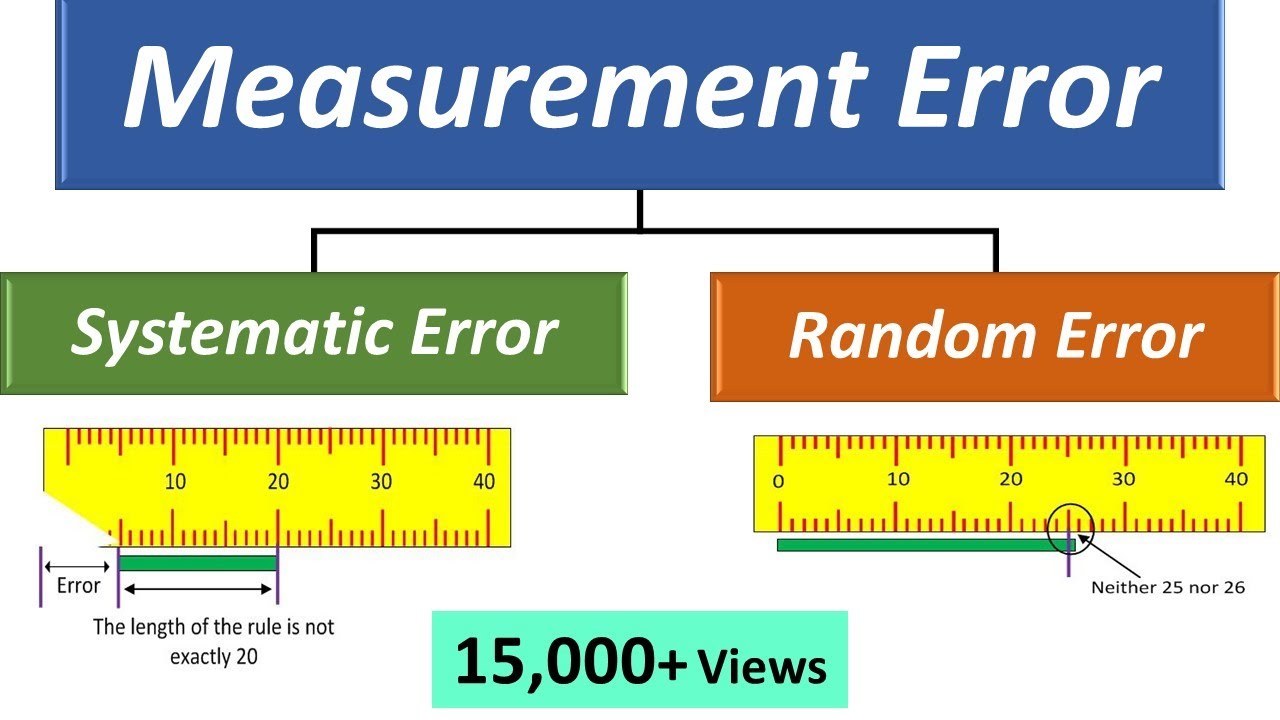
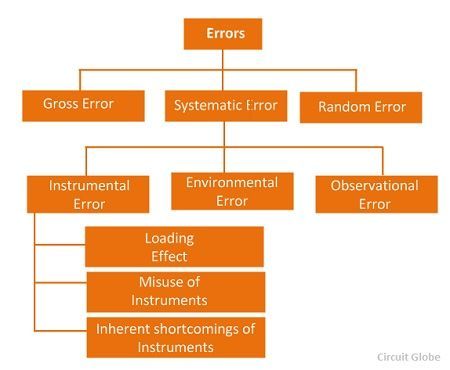
DEFINITION: Measurement error, which is the difference between the observed value and the variable’s true value, not observed, observed but for most variables. definition: Measurement error is defined as the difference between the true or value of the actual or measured value. The real quantity is the average value of infinity and the number of analysis, the measured value is the exact value. Errors that occur can come from a variety of sources and are generally classified into the following types. These types of errors
Their types are detailed below. There is a gross error of occurrence from the point of view of the humanfactor a. For example, if people using all instruments do or read incorrectly, they record their incorrect data. Such errors are blunders. Mistakes can probably only be avoided if you read everything carefully. For example: the experimenter usually reads 31.5°C, but the actual value is 21.5°C. This happens after the accident. The experimenter receives incorrect readings associated with an error that occurs throughout the measurement of everything. Errors of this type are surprisingly common in measurements. Is it possible to completely correct such typos? Some errors were noticed by the experimenter, but some are difficult to find. Two measures can eliminate a blunder. Two methods may well eliminate a blunder. These strategies Systematic errors mostly dividingdivided into several categories. This happens mainly for three main reasons. Congenital (a) instrument type defects – these defects arise due to their mechanical structure in embedded coatings. Can they be related to calibration, or manufacturing operation of the device. These errors can result in reading errors or high minification.if For example, a weak spring is used in the device, this gives a high value of the measured value. The instrument experiences errors due to friction or loss of hysteresis. (b) Dropped tool error – only happens because that proper tool is its operator’s error. A good tool, if not used wisely, can produce amazing results. Subtract one value from another. Yoube sure to divide the error by your actual exact or ideal value (not measured experimental value) or .Convert a decimal to a percentage by simply multiplying it by 100.Add a potential percentage symbol % to indicate your numerical error value. These problems are classified into three types, namely actual error, relative error and percentage error. Absolute error can be defined as the deviation between actual and measured values. Fout In MetingenWhat are measurement errors?
Measurement.error Types
1. Big Mistakes
How do you find the measurement error?
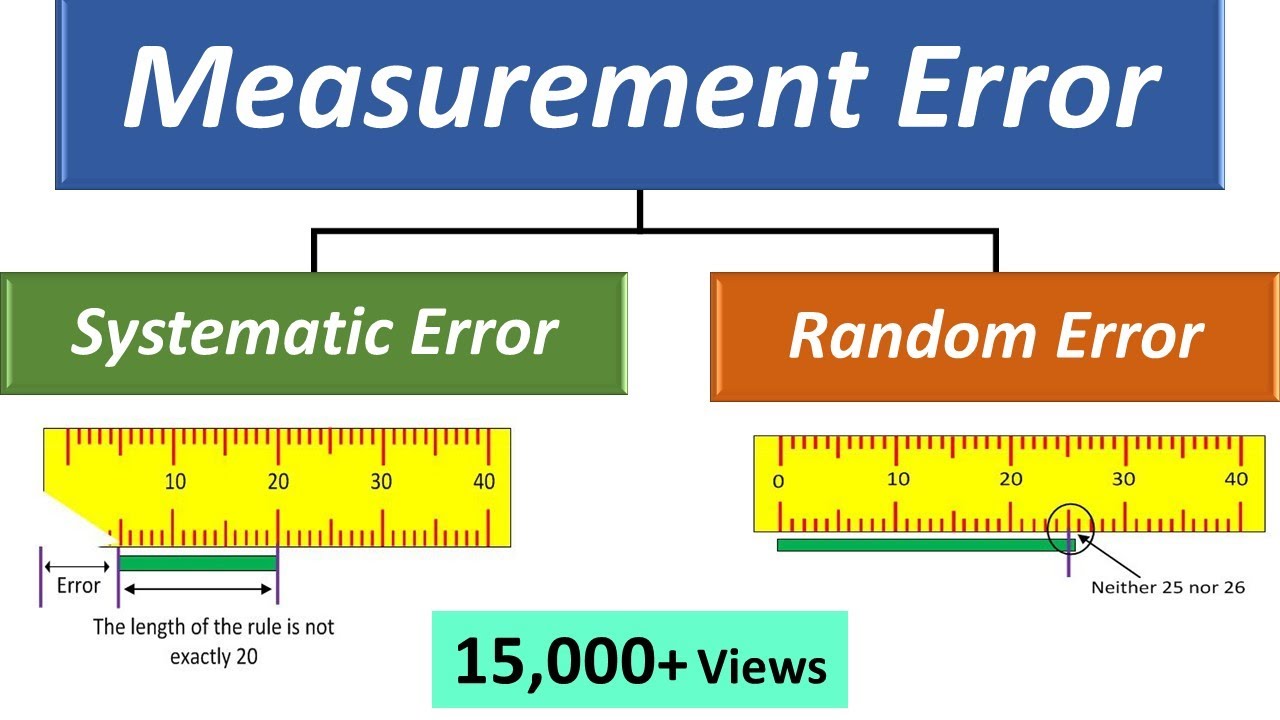
2. Systematic Errors
2 Errors
How do you find the measurement error?
What are the three measurement errors?
Erreur Dans Les Mesures
Fel I Mätningar
Ошибка в измерениях
Error En Las Medidas
Errore Nelle Misurazioni
Fehler Bei Messungen
측정 오류
Erro Nas Medições