Table of Contents
If you are seeing a linux kernel cache error code on your PC, take a look at these ideas for a solution.
Updated
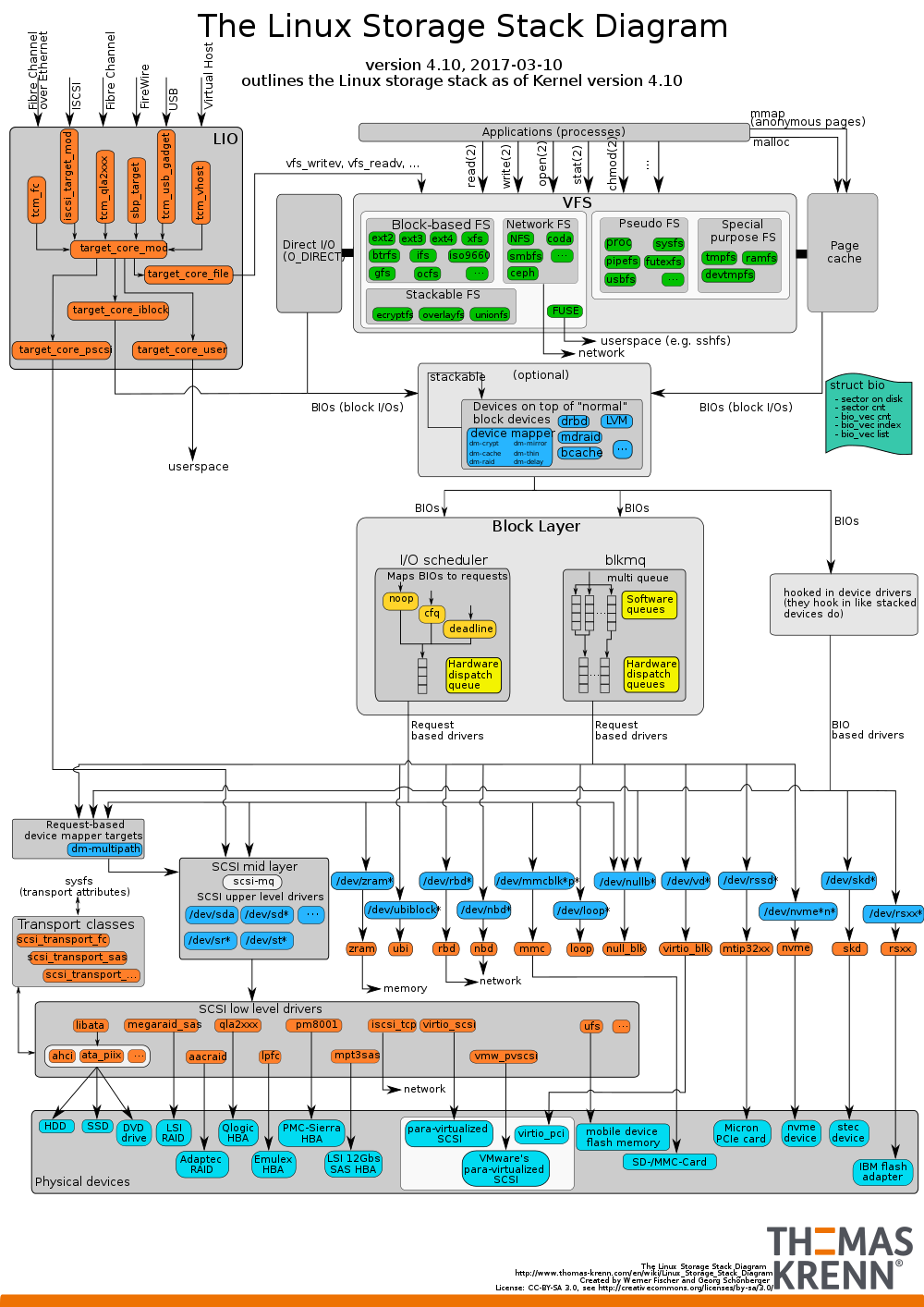
When managing memory, the Linux kernel uses a very own caching mechanism called page memory cache. Faster access to their content results in page caching and significant performance gains. The page cache is implemented in the kernel for every paging memory management and is mostly transparent to applications. https://en.wikipedia.org ›RSS Feeds› Corecache Page Cache – Wikipedia also includes a hard disk cache to improve read and write performance. In simple terms, its main purpose is to allow you to copy data and binaries into memory after they have been saved, which reduces memory I / O and improves overall performance.
This is a certain amount of system memory that a particular kernel reserves for caching the file scheme that the drive is accessing. This helps speed up primary performance. During Linux system read requests, the kernel checks if the cache consists of the requested data blocks.
Does Linux cache files in memory?
When it comes to memory management, the Linux kernel benefits from a built-in caching mechanism called page memory cache or disk cache to improve the performance generated by read and write operations.
Does Linux cache files in memory?
This takes a long time because Linux stores information about the type of cache used as a cache in unused areas of memory the first time it is read or written to storage media such as hard drives. If this data is then re-read, it can be quickly read from this cache in memory.
Page Cache Or Buffer Term, Cache
buffer cache, often used by page cache. Linux kernels prior to version 2.2 had both a page cache and a buffer cache. Since kernel 2.4 these two caches have been merged. As of today, there is only one cache, Page Cache.Linux [1]
How The File System Cache Works
The kernel reserves a certain amount of system memory to cache the most important imagesThe disk space in the file system to speed up the global cache in Linux is called the page cache. The page size is configurable for the memory cache, with generous defaults allowing statistics with large disk blocks to be cached. The Linux SystemUnix caching approach is known as write-back caching. This means that when data is written and the disk is written to memory, it is cache-mounted and marked dirty during caching until it is synchronized to support your disk. The kernel maintains internal data buildings that optimize the data to remove everything from the cache. If the cache needs more space.
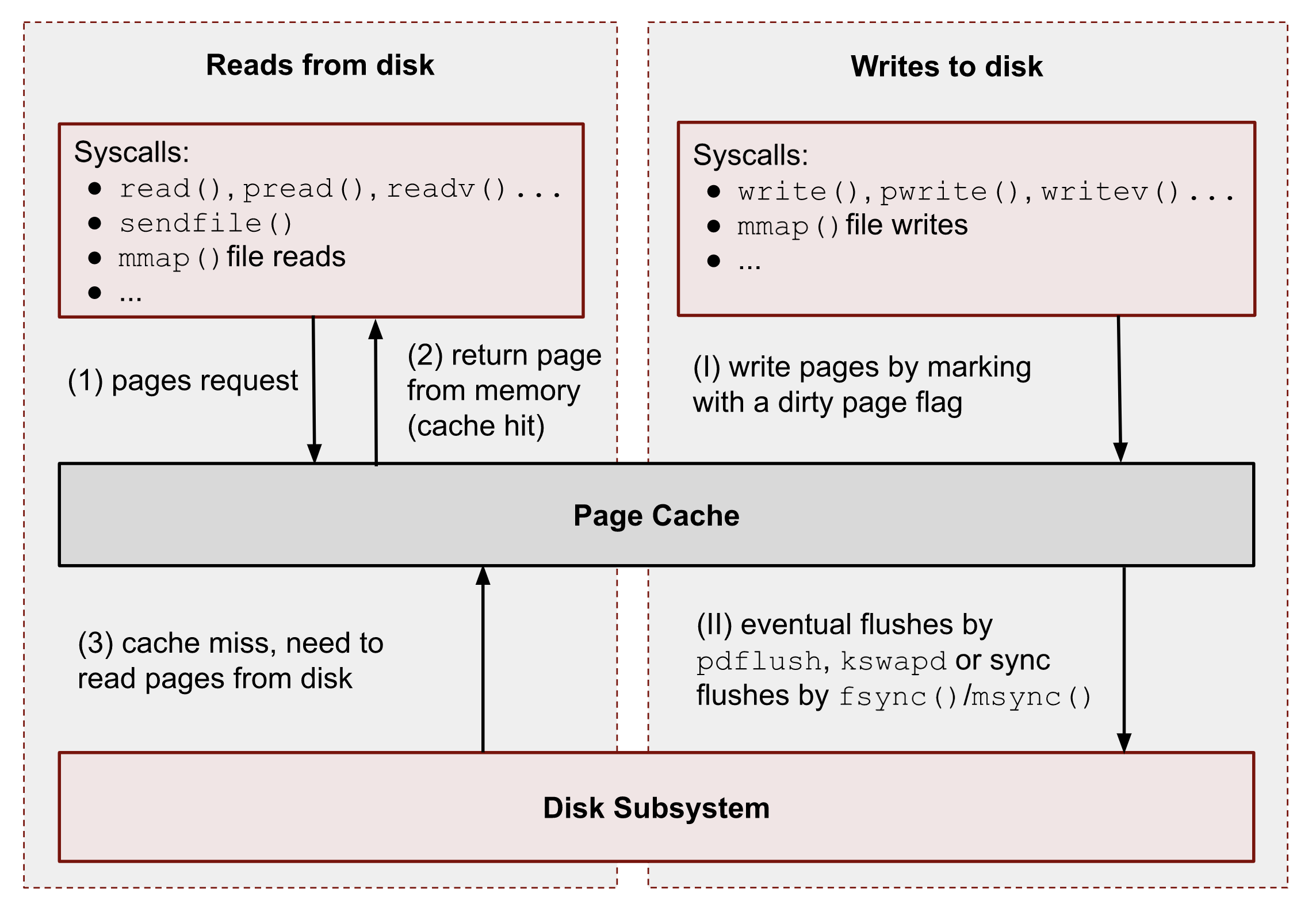
Review The Linux Very Cache Page
Brendan Gregg’s website is a good resource for tuning and measuring Linux performance. A tool called Knowing Cachestat is provided to measure the memory/cache ratio of Linux pageviews, which is part of the Perf-Tools GitHub flavor for SAP workflows. Each worker process uses approximately 200-300 MB of exclusive use.Memory calls, possibly when it is inactive. Most of the associated memory is shared between policies. The other part is the heap/job information itself.
How do I see cached memory in Linux?
cat to display information about Linux storage.free to display the amount of used physical space and paging space.Vmstat command to display virtual memory statistics.top Command for checking memory usage.htop to determine the memory usage of each process.
Speed up your computer today with this simple download.How do I view cached memory in Linux?
Compared to the /proc/meminfo file, a free query provides less information. However, it is incredibly easy to understand. The metric is clearly an available value as it indicates how much more memory is available to run better applications.
How do I clear cached memory in Linux?
Like any other operating system, GNU/Linux has efficient memory management and much more.other. But if some method is consuming your memory and your company wants to clear it, Linux offers a special way to clear or clear the good old RAM cache.
Is it safe to clear cache memory in Linux?
Sometimes a new system runs out of memory because huge amounts of RAM are being used by real cached physical objects. In these cases, you need to either increase the system’s physical memory or add more swap space. You can also tell the kernel to drop the RAM cache on the system by adding the number found in /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches.
How does disk caching work in Linux kernel?
The Linux kernel uses available memory for disk caching if some of it is not required by the application. This improves the bet a bit. When there are no more pages available in physical memory, the kernel swaps out some previous pages to disk. 1 time ago this cache memory was 3 GB.
Linux-Kernel-Cache-Speicher
Memória Cache Do Kernel Linux
Linux Kernel Cache-minne
Pamięć Podręczna Jądra Linux
Linux 커널 캐시 메모리
Linux Kernel Cache Geheugen
Mémoire Cache Du Noyau Linux
Memoria Caché Del Kernel De Linux
Memoria Cache Del Kernel Linux
Кэш-память ядра Linux