Table of Contents
Updated
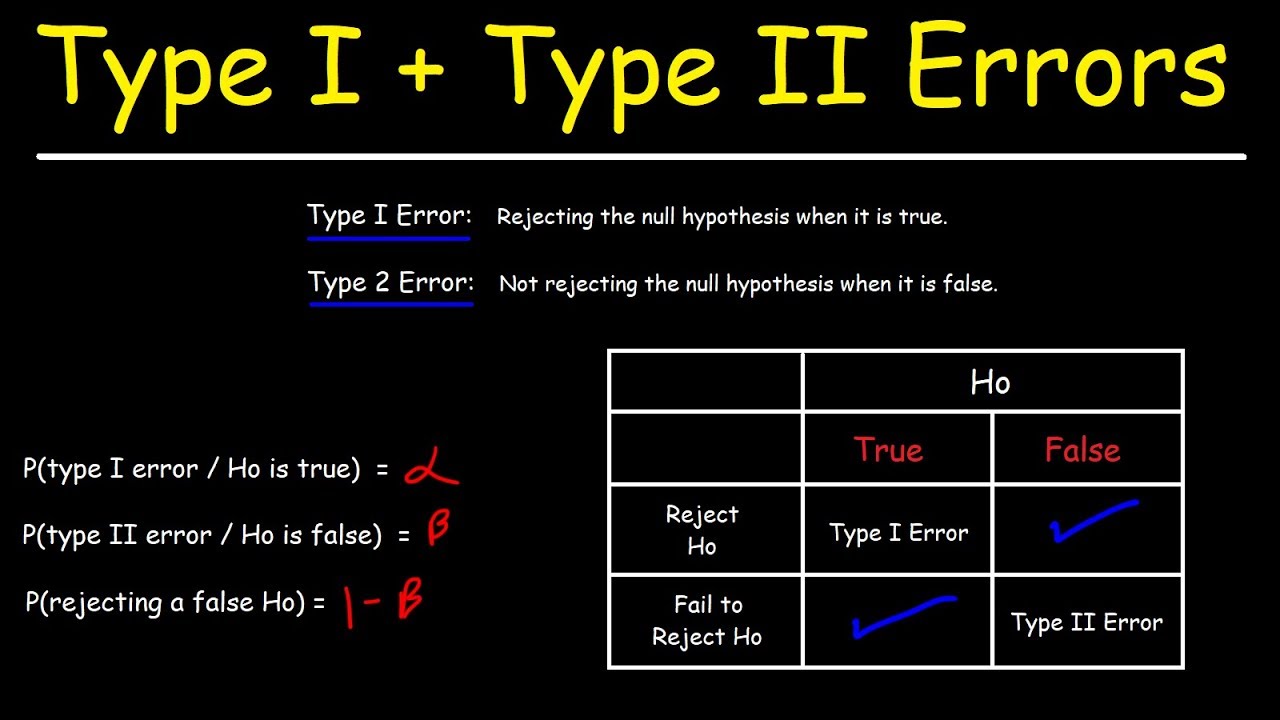
This guide will describe some of the possible causes that can lead to Type 1 error statistics, and then I will highlight some potential recovery methods that you can try to fix the problem. g.A specific type 1 error, also known as a false supervisor, occurs when a researcher mistakenly denies a true null hypothesis. This means that you are reporting that your results are great when in fact they are the result of chance. For example, a p-value of 0.01 would mean there is a true 1% chance of making a Type I error.
g.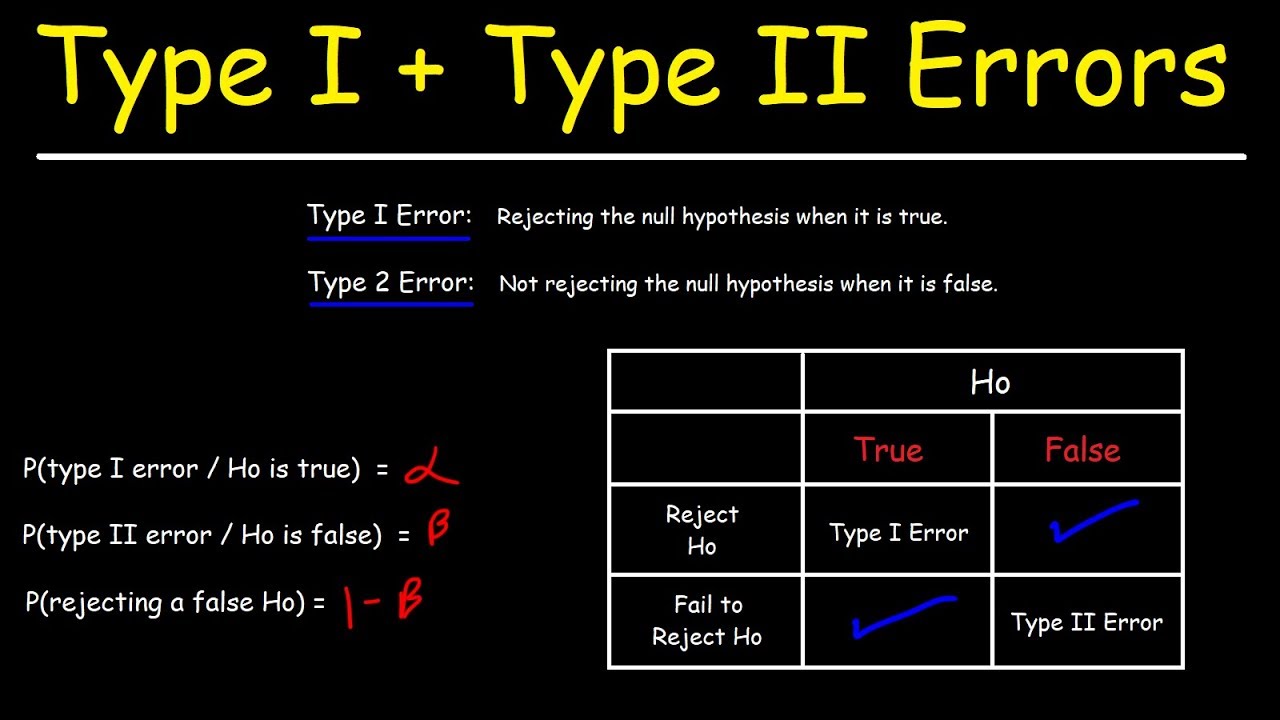
Statistical hypotheses confirm that no method can be 100% guaranteed: this is simply because we rely on probabilities when you want to experiment.
When internet marketers and academics study hypotheses, they both look for statistically significant results. This means that the results must be correct over a range of probabilities (usually 95%).
While testing assumptions are believed to be good, there are usually two types of errors.
These are errors known as You and Type 2 errors (Type I errors, not to mention Type II errors).
What Are Type 1 Errors
How do you determine type 1 error?
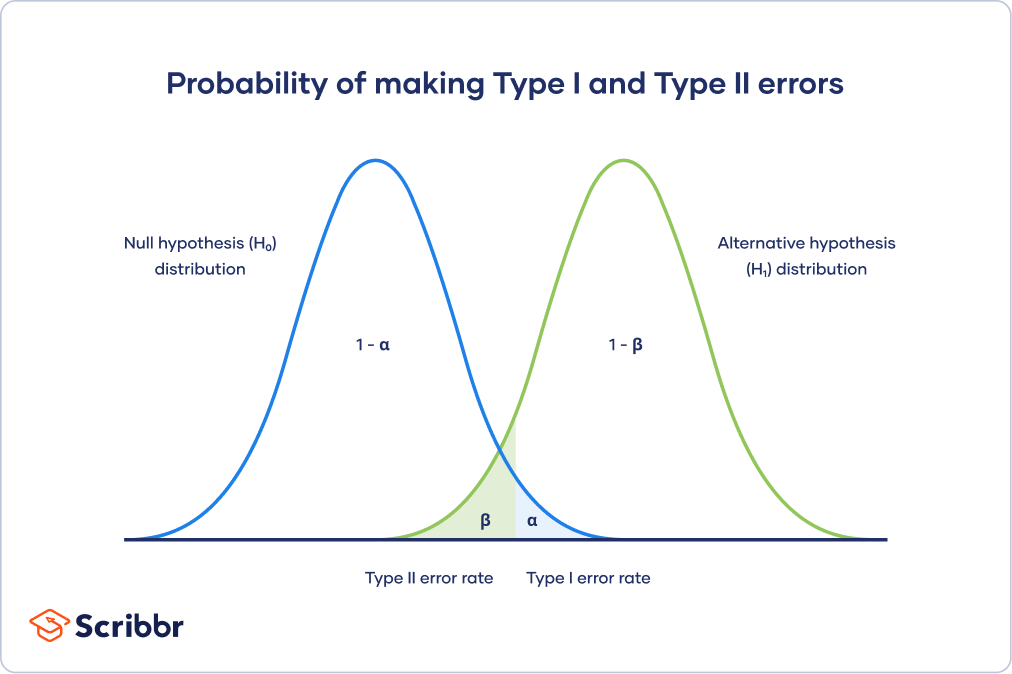
A type I error means that if the null hypothesis is indeed sincere, it will be rejected. It can be concluded that the results have passedand statistics are significant when in fact they are more or less the result of chance or insignificant factors. The risk of error is the level of significance you choose (alpha or pre-alpha).
Errors of the first type, which are often called fakes, occur when testing hypotheses, when the null hypothesis is generally correct, but the phenomena are rejected.
Simply put, type 1 problems are “false – positive” when all testers confirmexpect a statistically significant difference when there is none.

Errors of the same type have a probability of “±”, which corresponds to the confidence level you set. A test with a certain confidence level of 95% means that there is a 5% chance of getting a certain error.
Consequences Of Type 1 Error
Updated
Are you tired of your computer running slow? Annoyed by frustrating error messages? ASR Pro is the solution for you! Our recommended tool will quickly diagnose and repair Windows issues while dramatically increasing system performance. So don't wait any longer, download ASR Pro today!

Errors of type 12 can occur with a high probability (5% probability paid off) or because you did not adhere to the duration and sample size originally defined for your experiment.
Therefore, an error of type 1 can lead to false positives. This implies that you mistakenly believe that the hypothesis test worked when it did not. Real
In real life situations, this can mean that potential sales are missed due to an obvious false assumption caused by the test.
Real Life Circumstances Associated With Suspected Type 1 Error
Let’s say you want to increase the number of conversions on a banner on your website. WhatIf it worked, you planned to add an image to see if it would increase conversions or not.
You start your A / B test by running version (A) that is hostile to version (B) and contains its appearance. After 5 days, option (B) usually outperforms control version a because it confuses the 25% increase in conversion with 85% confidence.
You stop the test and change the image in your banner. However, in the new month, you notice that the number of conversions has dropped from month to month.
This is because you have a bug like this: 1 Your strain often does not hold up to your long-term control version.
What Are Type II Errors
If at least one error is often referred to as “false positive”, type 2 errors are referred to as “false negatives”.
Type 2 errors happen when you mistakenly assume that a winner has not been announced between the baseline and the baseline, when in fact there are almost all winners.
Statistically, exact type 2 errors occur when the null hypothesis is artificial. th, and does not arise afterwards.
If the likelihood of making a type a specific type is an error defined by “±”, a type 2 possibility is an error in evaluating “²”. Beta depends on the strength of the overall test (ie, on the probability of not assigning an error of type 2, resulting in 1-).
There are 3 parameters that can affect test performance:
- Music size (s)
- Significance level of your test drive (Î ±)
- “Real” value of the confirmed parameter (more details here)
Consequences Of Type 7 Error
Like type 1 errors, data entry errors can lead to wrong assumptions and bad decisions that can only lead to lost sales or reduced profits.
In addition, an actual false negative result (without even realizing it) can discredit your conversion optimization efforts, even if your company could validate your hypothesis. Could this be a daunting turning point for all CRO experts as digital marketers?
Specific Example Of Unsuccessful Playproduction
For example, let’s say you’re running an e-commerce business that sells sophisticated, high-quality electronic products to tech-savvy customers. To directly increase the number of conversions, you need to customize the FAQ section on your gadget page.

You run an A / B experiment digitally to see if option (B) can outperform your control version (A).
On the calendar, you see no difference in sales: in both versions, fears seem to change at the same time, and you start to doubt your hypothesis. After three days, cancel the test and save your product form as it is.
At this point, you’re getting closer to adding the FAQ to your repository without impacting conversions.
Two months later, you find out that a competitor may have created an FAQ at the same time and noticed a noticeable increase in conversions at the same time. You decide to retake the whole test a month to get more mathematically relevant results based on an increased confidence concentration (eg 95%).
After a month, which is a big surprise, you will see a positive increase in conversion rates for option (B). Adding FAQs at the end of your product URL actually gave your business more promotion than the review version.
Correct – the first test encountered a Level 2 error!
Speed up your computer today with this simple download.
What is a Type 1 error in statistics example?
Examples of type I errors Zero speculation that a person is innocent, for a long time the alternative is to blame. A Type I error in this case would mean that the person not found innocent will go to prison, even if at this stage he is actually innocent.
How do you determine Type 1 and Type 2 errors?
A type I (false positive) error occurs when the same researcher rejects a null hypothesis that is unambiguously true for a population; A Type II (false negative) correctness error occurs when the researcher does not reject the null theory, which is actually false in nature.
Comment Corriger Les Statistiques Des Erreurs D’identification De Type 1 ?
Wie Behebe Ich Die Statistik Von Typ-1-Identifikationsfehlern?
Hoe Los Ik De Statistieken Van Type 1 Identificatiefouten Op?
Hur åtgärdar Jag Statistiken För Identifieringsfel Av Typ 1?
Jak Naprawić Statystyki Błędów Identyfikacji Typu 1?
유형 1 식별 오류의 통계는 어떻게 수정합니까?
¿Cómo Soluciono Las Estadísticas De Errores De Identificación De Tipo 1?
Como Corrijo As Estatísticas De Erros De Identificação Do Tipo 1?
Как исправить статистику ошибок идентификации 1-го типа?
Come Posso Correggere Le Statistiche Degli Errori Di Identificazione Di Tipo 1?